High molecular weight polyethylene glycol (PEG) with a single structure.

Single-structure, high-purity polyethylene glycol (PEG) derivatives with no molecular weight distribution can be synthesised.
Commercially available polyethylene glycol is a mixture of polymers obtained by polymerising monomers such as ethylene oxide, which are separated into
mixtures by approximate molecular weights. The separation of structures with similar molecular weights becomes impossible as the molecular weight increases.
For this reason, polymeric PEG with a molecular weight above 1,000 has a molecular weight distribution with a molecular weight variation of ±10-30% ( PDI = 1.02-2).
The average molecular weight is generally used as the trade name, e.g. PEG-1.4 (average molecular weight 1,400), PEG-2K (average molecular weight 2,000).
Our products are synthesised in a completely different way and have a single structure.
Advantages of using high purity (single product) PEG compounds
- Structure-activity relationship studies can identify the optimum PEG molecular weight.
- The single structure of PEG provides sharp chromatograms without tailing, facilitates the removal of unreacted raw materials and by-products in the purification step of intermediates, and reduces the possibility of impurities other than PEG.
- Excellent repeatability with minimal variation in quality from batch to batch.
Disadvantages of high purity products (single products)
- The price rises steeply with increasing molecular weight. Applications are limited as they can only be used in minute quantities.

We refer to this compound as Tos-PEG27-OH, which is a way of describing the number of ethylene oxide repeating units with the functional groups at either end.
More information on our PEG nomenclature.(written in Japanese)

Comparison of our products with those on the market
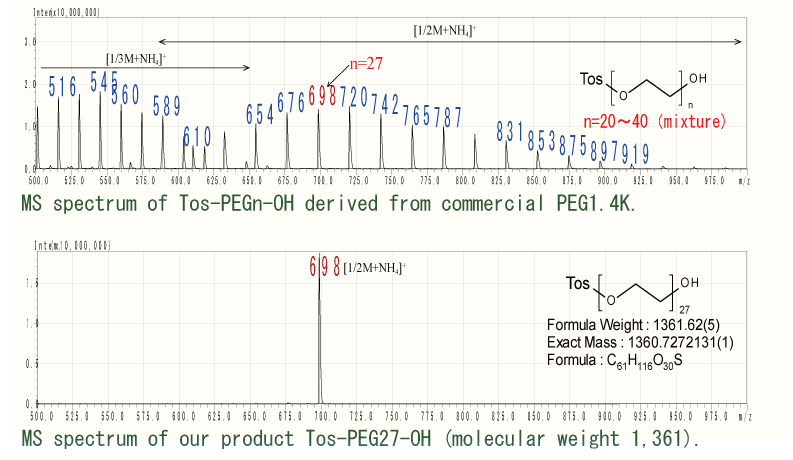
As our product is a single product, only the signal corresponding to molecular weight 1,361 (1/2M Ammonium adduct ion: m/z = 698) is detected in the above MS spectral data, Impurity signals with different repeat units are not detected.
On the other hand, MS spectral data confirm that commonly available PEG derivatives are mixtures of various molecular weights.
One unit of ethylene oxide is 44 MS, so in the 1/2 MS region signals are observed at equal intervals of m/z = 22.
MS spectra show that commercial products range in molecular weight from about 1,000 to 2,000 and that the major component, Tos-PEG28-OH, is at most a few per cent.
Even 'high purity' products synthesised by polymerisation have a slightly narrower molecular weight distribution and are mixtures containing impurities with different repeat units.
(Repetition unit around 20: PDI=1.00001 is the limit even with molecular weights lower than 1,000... Polym.Chem.,2014,5,694)
 PDI: A number greater than 1.0; the closer to 1.0 (more zeros below the decimal point), the sharper the molecular weight distribution.
PDI: A number greater than 1.0; the closer to 1.0 (more zeros below the decimal point), the sharper the molecular weight distribution.

The advantages of using high purity products (single products) are
 Structure-activity relationship studies can identify the optimum PEG molecular weight.
Structure-activity relationship studies can identify the optimum PEG molecular weight. Sharp chromatograms without tailing due to a single structure, easy removal of unreacted raw materials and by-products in the purification step of intermediates, low possibility of contamination with impurities other than PEG.
Sharp chromatograms without tailing due to a single structure, easy removal of unreacted raw materials and by-products in the purification step of intermediates, low possibility of contamination with impurities other than PEG. The same quality can always be provided and quality differences between lots are small and reproducible.
The same quality can always be provided and quality differences between lots are small and reproducible.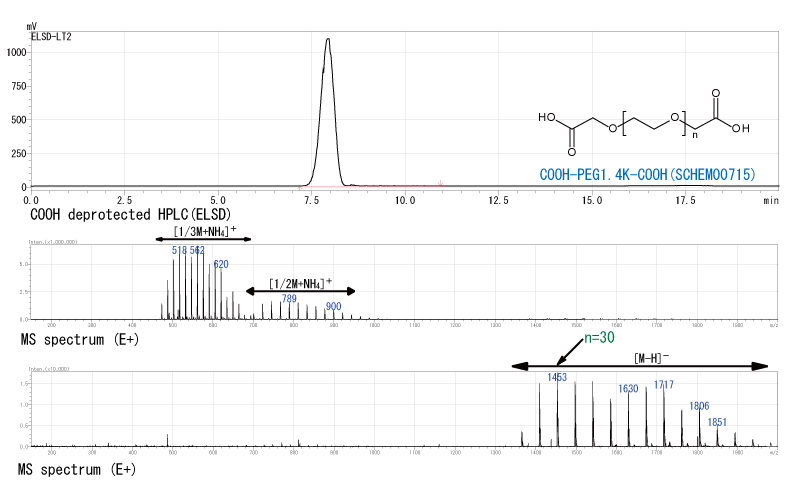
Our product has a single structure and therefore has a simple MS spectrum as described above.
Lot 2 has a broad peak shape and a wider molecular weight range in the MS spectrum compared to Lot 1.
Commercially available PEG derivatives that are not a single product (with a molecular weight distribution) can vary significantly in quality between different lots, even with the same average molecular weight.
Our highest molecular weight structure currently synthesised is a PEG repeat unit n=220 (OH-PEG-OH equivalent molecular weight 9,698 PDI=1.000004).
Since the synthesis method has been established, it is possible to synthesise even higher molecular weight PEGs and is currently being developed for high molecular weight PEGs with a molecular weight of over 20K.
(Figure below, mono-Trt protected polyethylene glycol: repeat unit 220 LC/MS analysis data).
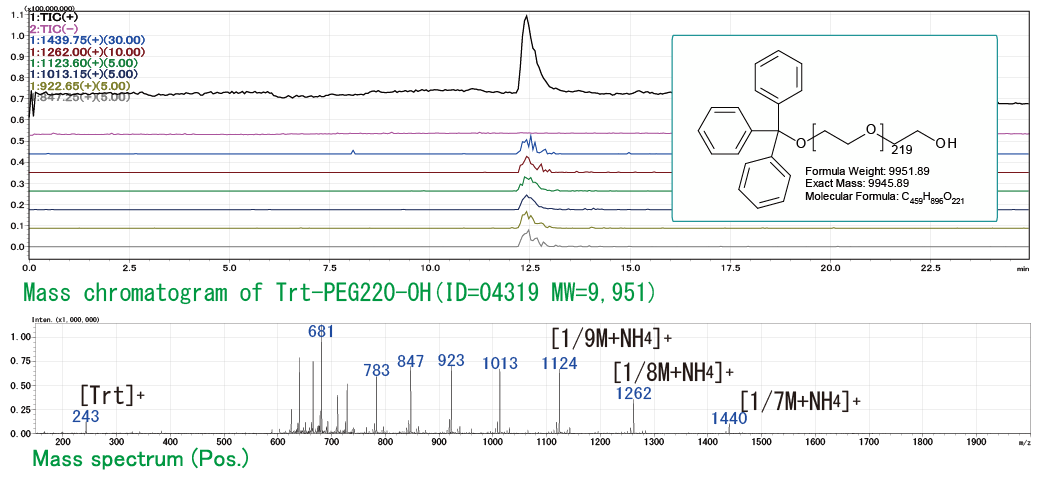
It can be derived from one-sided Trityl-protected PEG (Trt-PEGn-OH) to provide various functional groups at both ends and has a track record of synthesising more than 500 polyethylene glycol derivatives.
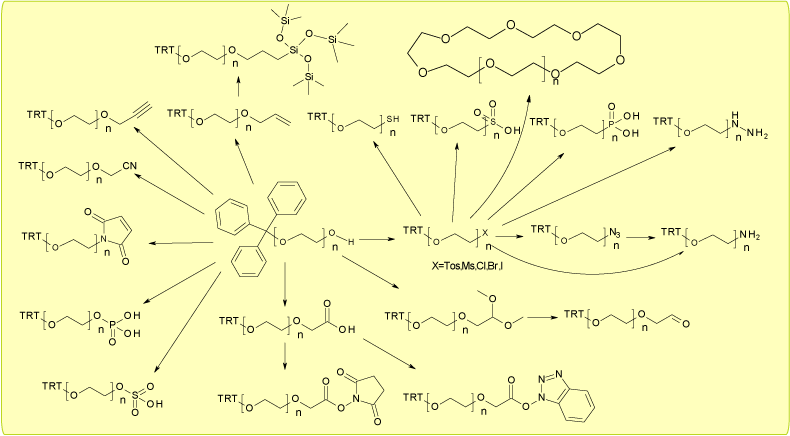
Ultra-pure PEG synthesis technology is applied and has a proven track record in the derivation of various functional groups.
PEG-related technical documents
- Mono-disperse polyethylene glycols(TD001)

- PEG hybrid compounds(TD025)

- PEG linker that can be cleaved under mild conditions(TD030)(not ready)

- macrocyclic crown ether(TD034)

- Fluorescently labelled PEG molecular weight markers(TD036)

- Crown ether with branches(TD037)

- Cyclodextrins with PEG linkers(TD042)

- Synthesis of dyes with PEG linkers and fluorescent dyes(TD048)

- Functionalisation of each end of PEG Linker(TD049)

- Spacers and cross-linkers(TD050)

- PEG dicarboxylic acid derived from commercial PEG(TD054)

- Diamino PEG derived from commercial PEG(TD055)

- HaloTag HaloLinker (HaloTag HaloLinker)(TD066)

- List of PEG derivatives

- List of fluorescently labelled PEG derivatives

Molecular weight distribution is not an issue and lower cost is a priority.
We have received a lot of requests, so we got down to business.
Weigh up the advantages and disadvantages of each of the single products and mixtures before choosing the right derivative for your research.
Advantages of commercial PEG derivatives.
- Relatively low prices.
Disadvantages of derivatives from commercial PEG: it is the flip side of the coin with single products.
- Depending on the functional groups at both ends of the PEG molecule, identification is generally difficult at molecular weights above 2,000 and almost impossible at molecular weights above 4,000.
- As a mixture, the peaks are broad compared to single structures. Not only does this increase the difficulty of purification, but also increases the likelihood of impurity contamination.
- Quality varies from batch to batch. Even if the same raw material is used and the same crude is purified on the column, the molecular weight range will vary slightly depending on where and how far from the main peak the crude is recovered.
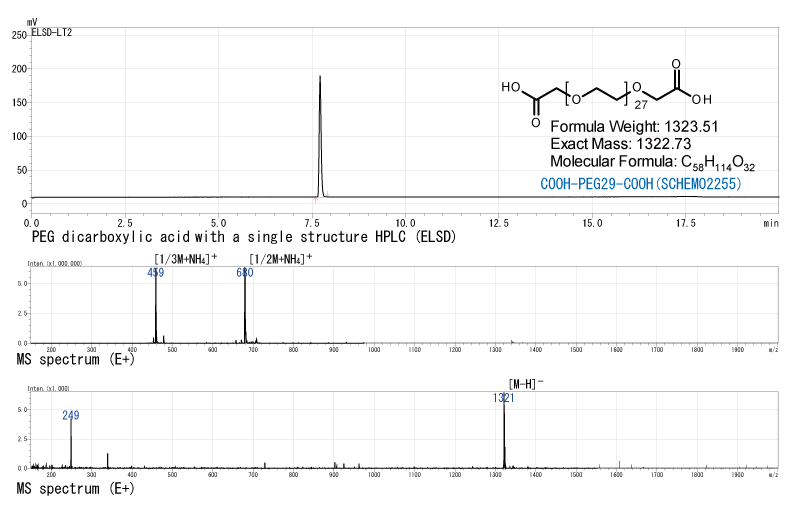
 Dicarboxylic acid derived from commercial PEG.
Dicarboxylic acid derived from commercial PEG.
 Diamino derived from commercial PEG.
Diamino derived from commercial PEG.

